When we talk about Industry 4.0 we all refer to the Fourth Industrial Revolution. A new challenge for the society and the world industrial production. The previous three industrial revolutions were in the order: the mechanical revolution of the 18th century, the electric revolution of the nineteenth century and the most recent electronic revolution in the second half of the twentieth century. Today, industry is in a real digital revolution that streamlines and makes production processes more and more efficient.
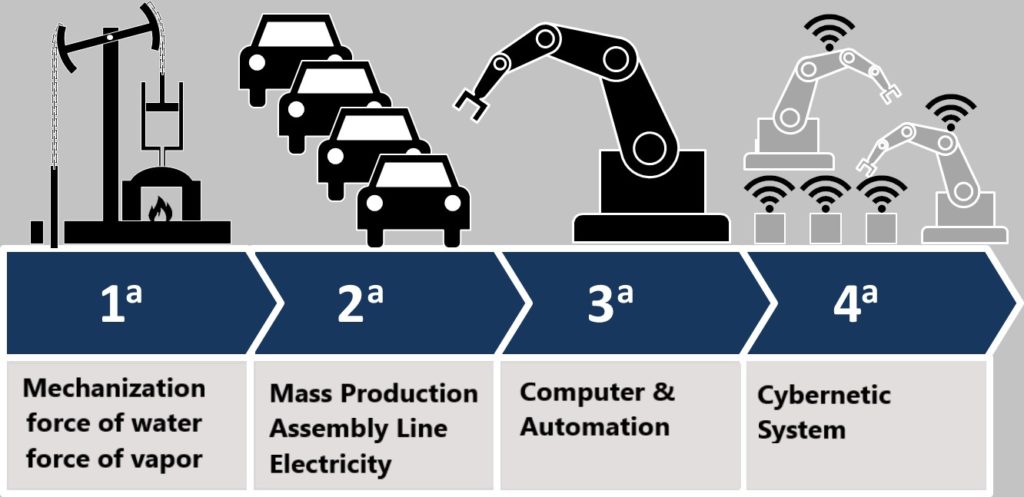
What are the new technologies
The entire economic sector is invested by the Industry 4.0 revolution and by the consequent technological transformation. Technological transformation takes place through the development of processes and devices capable of processing a huge mass of data in very short times. In addition, these data are supported by multitasking machines that perform complex tasks that, up to now, were only made by human operators. Among the technologies that distinguish industry 4.0 are:
- “Big Data”, the availability of a huge mass of data stored on devices that allow process and transmission at unbelievable speeds.
- “Internet of the Things” also said web 4.0, the possibility of connecting different objects between them. The “connected” objects can learn from the surrounding environment by using sensors and transmitters.
- “Cloud Manufacturing” is the data and resources of industrial production that are immediately available and accessible upon request by those companies that interact through a global network.
- “Advanced Automation” robots that become ergonomic and capable of processing and learning information, able to solve complex problems.
- “Wearables” and Voice Interfaces, all the technologies that increase human capabilities such as the benefits of using robotics in surgery.
- “Additive Manufacturing” technology that allows adding material rather than removing it with consequent benefits for the environmental impact of the current industrial productions. A great example is the 3D printing.
Obstacles to Industry 4.0 (Italian case)
The main obstacle to this revolution is the missing step of business towards digitalization. Let’s take as an example the Italian case. It is estimated that only 4.7% of GDP in Italy consist in digital investments, compared with a 6.4% of European average. The gap in digital investment in Italy compared to the European average is 25 billion euros per year. For this reason, important steps must be taken to help Italy to achieve this goal and reduce the gap. In addition, these efforts will help Italy not to lose the competitiveness of its business system.
Necessary investments
To be able to keep up with the revolution and adapt to new ways of conceiving the industry, the entire economic system requires significant investment in Research, Development and Innovation. Investments that the industry needs both at the human capital and at the technological levels. Italy has launched a series of massive incentives for italian companies to upgrade their production system for the three-year period 2017-2020.
The incentives will allow companies to refresh their own workshops, often equipped with obsolete machinery. From the point of view of human capital, technological progress must be accompanied by increasingly up-to-date and qualified staff. Effort is required both for entrepreneurs and universities.
Entrepreneurs should be able to handle the transition from the traditional way of producing to a digital innovation. On the other hand, Universities should train students in the right direction and make certain courses more attractive.
The positive case of German industry
The German business model has always been regarded as the ideal model for industrial production. Today, this belief is even stronger because German companies understood before all that they had to take the road drawn by Industry 4.0.
The strong point of the German model has been the fact that it is possible to focus on the presence of medium-sized companies and on the ability to take advantage of integrated production chains. The key to success was therefore the predisposition of German companies to make and support all kinds of aggregating forms. This has quickly promoted the development of a reliable and fast network infrastructure capable of spreading digital technologies in industrial districts in a relatively short timeframe.
Support from the European Community
To support Industry 4.0, a strong intervention by the European Union is also needed. It is necessary to intervene in the standardization of production processes and actors involved. This type of intervention is necessary to promote the real integration of large scale production chains and industrial districts within the European market and not.
Last analysis
Industry 4.0 is not just a concept, but a reality that comes from a real revolution. Like all revolutions, actors involved need to be transformed and adapted to the changing. The need to adapt to changes is therefore crucial for companies wishing to maintain and strengthen their competitiveness on the market.
If you are interested in buying used machine tools and used packaging and processing machines, have a look on our online catalogue or feel free to contact us!

